Okio
封装InputStream和OutputStream为Source和Sink,提供了一些列高效读写字节和字符的方法;
基本使用
向File中写入数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10String name = "xiaoming";
int age = 11;
try {
Okio.buffer(Okio.sink(file)).writeUtf8(name).writeInt(age).close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}文件拷贝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22try {
/**
* 当同时存在Source和Sink时,不建议完全采用链式的调用,因为source、sink在结束时必须关闭;
* 小心使用writeAll,因为writeAll并不会返回Sink,所以采用链式调用最后没法直接close;
*
* 对于压缩文件,如果在最后没有调用close将流正确关闭,则会损坏到压缩文件
*/
// Okio.buffer(Okio.sink(destFile)).writeAll(Okio.buffer(Okio.source(srcFile)));
BufferedSink sink = Okio.buffer(Okio.sink(new File(filePath)));
BufferedSource source = Okio.buffer(Okio.source(in));
sink.writeAll(source);
sink.close();
source.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (IOException ex){
ex.printStackTrace();
}
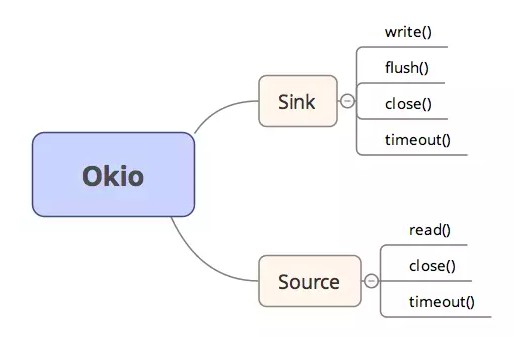
Source
对应原生IO的InputStream,提供字节流数据,通过source,可以从网络、存储、内存等地方读取到数据流;
提供了read方法,支持Sink读取数据到其Buffer缓存中;
一般情况下,不要直接操作Source,而是操作BufferedSource,它提供了更丰富、高效的接口;
Source还提供了一个强大的skip方法(BufferedSource),能让我们跳过指定数量的字节后,再读字节流;
1 | public interface Source extends Closeable { |
BufferedSource
带有缓存的Source接口,实际实现是RealBufferedSource;
Sink
对应原生IO的OutputStream,提供了write方法,用来从Source缓存中读取缓存数据,写入到自己的
Buffer缓存中;一般情况下,不要直接操作Sink,而是操作BufferedSink,它提供了更丰富、高效的接口;
Sink能够代替DataOutputStream(写入原生数据)、BufferedOutputStream(写入缓存数据)、
OutputStreamWriter(数据流字符编码);在结束时,必须调用Sink的close方法,将缓存数据推送进目标中,并且释放调用持有的资源(在采用
链式调用时,需要注意最后也需要关闭Sink);
通过:1
Okio.buffer(Sink);
可以得到BufferedSink实例;
1 | public interface Sink extends Closeable, Flushable { |
BufferedSink
带有缓存的Sink接口,实际实现是BufferedSink类;
Segment
Segment字面的意思就是片段,okio将数据也就是Buffer分割成一块块的片段,内部维护者固定长度的
byte[]数组,同时segment拥有前面节点和后面节点,构成一个双向循环链表;
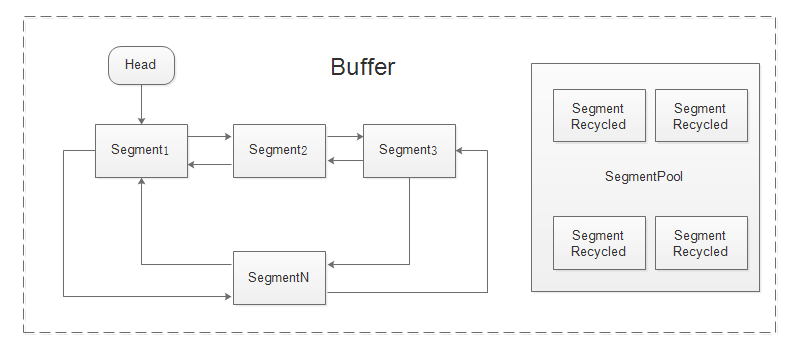
- 采用双向链表的解构,每一个Segment都代表一个节点,并且保存了前后两个节点的指针,
提供了pop(出栈)和push(入栈)方法; - 封装了一个byte数组,用来保存一小段缓存数据;
- 多个Segment之间可能会分享数据流,在这种情况下的Segment,可能无法被回收和修改;
- pop方法用来将当前Segment从当前链表中移除,push方法用来将一个Segment添加到当前Segment的
后面;
属性:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33/** The size of all segments in bytes. */
static final int SIZE = 8192;
/** Segments will be shared when doing so avoids {@code arraycopy()} of this many bytes. */
// 在调用split分割Segment时,如果要求分割的字节数超过了该值,则不会采用复制数组的方式进行
// 分割,而是采用共享的方式
static final int SHARE_MINIMUM = 1024;
final byte[] data;
// Segment保存的字节数组中,第一个可读的位置
/** The next byte of application data byte to read in this segment. */
int pos;
// Segment的剩余可写的字节数组的第一个位置
// 所以Segment实际保存的数据为pos ~ limit-1
/** The first byte of available data ready to be written to. */
int limit;
// Segment的字节数据是不是与别的Segment共享的,默认情况下是false
// 当在split时采用的是共享的方式,则分割出来的Segment该变量为true
/** True if other segments or byte strings use the same byte array. */
boolean shared;
// 当前Segment是否是其中字节数据的拥有者
/** True if this segment owns the byte array and can append to it, extending {@code limit}. */
boolean owner;
/** Next segment in a linked or circularly-linked list. */
Segment next;
/** Previous segment in a circularly-linked list. */
Segment prev;
pos和limit变量类似于两个指针,在Segment进行字节数据共享时,这两个变量用来指定当前Segment
有效的数据域(范围),这也是为什么,当多个Segment共享字节数据时,Segment无法被修改。如果修改了,
那么其他的Segment的有效数据域可能会受到影响;
- sharedCopy
创建一个新的Segment,这个与创建它的Segment共享同一个字节数组数据,并且标明这个新的Segment不是
字节数组数据的拥有者;1
2
3
4Segment sharedCopy() {
shared = true;
return new Segment(data, pos, limit, true, false);
}
- unsharedCopy
创建一个全新的Segment,并且这个Segment的数据与创建它的Segment是相同的;1
2
3Segment unsharedCopy() {
return new Segment(data.clone(), pos, limit, false, true);
}
- pop
将当前Segment从链表中移除;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8public @Nullable Segment pop() {
Segment result = next != this ? next : null;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
next = null;
prev = null;
return result;
}
- push
将Segment添加到当前Segment之后;1
2
3
4
5
6
7public Segment push(Segment segment) {
segment.prev = this;
segment.next = next;
next.prev = segment;
next = segment;
return segment;
}
- split
根据传入的字节数,分割Segment,将新分割出来的Segment添加到当前Segment之前;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28public Segment split(int byteCount) {
if (byteCount <= 0 || byteCount > limit - pos) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
Segment prefix;
// We have two competing performance goals:
// - Avoid copying data. We accomplish this by sharing segments.
// - Avoid short shared segments. These are bad for performance because they are readonly and
// may lead to long chains of short segments.
// To balance these goals we only share segments when the copy will be large.
// 如果分割的字节数超过了1024,则采用共享字节数组的方式
if (byteCount >= SHARE_MINIMUM) {
prefix = sharedCopy();
} else {
// 否则直接创建一个新的Segment,并复制数据
prefix = SegmentPool.take();
System.arraycopy(data, pos, prefix.data, 0, byteCount);
}
// 如果采用共享数据的方式,data数据拥有者的pos最大不会超过limit
// 如果是共享数据的方式,分割后的两个Segment实际是通过pos和limit来分别指向同一个字节数组的
// 不同数据段
prefix.limit = prefix.pos + byteCount;
// 当前Segment的pos重新指向
pos += byteCount;
// 将分割出去的Segment放到前一个Segment的后面,也就是当前Segment的前面
prev.push(prefix);
return prefix;
}
- compact
合并当前Segment和它之前的Segment为一个;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public void compact() {
if (prev == this) throw new IllegalStateException();
if (!prev.owner) return; // Cannot compact: prev isn't writable.
int byteCount = limit - pos;
// 如果prev是与别的Segment共享字节数组的,则其只能使用从limit~SIZE的部分
// 否则,0~pos部分也是可以使用的,当然,一般情况下,pos是等于0的
int availableByteCount = SIZE - prev.limit + (prev.shared ? 0 : prev.pos);
if (byteCount > availableByteCount) return; // Cannot compact: not enough writable space.
// 开始合并到prev中
writeTo(prev, byteCount);
// 移除当前Segment
pop();
SegmentPool.recycle(this);
}
- writeTo
将指定字节数的数据移到Sink中;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public void writeTo(Segment sink, int byteCount) {
if (!sink.owner) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// sink从limit~SIZE的部分不足以放入当前Segment,则检查Sink的0~pos部分是否可以放入数据
if (sink.limit + byteCount > SIZE) {
// We can't fit byteCount bytes at the sink's current position. Shift sink first.
// 虽然Sink是其字节数组的拥有者,但是其字节数组一部分是与别人共享的,这部分共享的数据,
// 可能使用了0~pos的部分,所以这部分不能被修改
if (sink.shared) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 加上前面的pos部分也不足以将当前Segment数据移进Sink中
if (sink.limit + byteCount - sink.pos > SIZE) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 将sink的字节数组数据移到pos = 0的位置
System.arraycopy(sink.data, sink.pos, sink.data, 0, sink.limit - sink.pos);
sink.limit -= sink.pos;
sink.pos = 0;
}
// 将当前Segment的数据移到Sink中
System.arraycopy(data, pos, sink.data, sink.limit, byteCount);
sink.limit += byteCount;
pos += byteCount;
}
ByteString
ByteString内部可以保存byte类型的数据,作为一个工具类,它可以把byte转为String,这个String可
以是utf8的值,也可以是base64后的值,也可以是md5的值等等;